| CATEGORII DOCUMENTE |
| Bulgara | Ceha slovaca | Croata | Engleza | Estona | Finlandeza | Franceza |
| Germana | Italiana | Letona | Lituaniana | Maghiara | Olandeza | Poloneza |
| Sarba | Slovena | Spaniola | Suedeza | Turca | Ucraineana |
Even during the present slowdown, networked companies are outperforming conventional ones. They are likely to go on doing so.
When Cisco Systems
announced a $2.2 billion inventory write-down in the second quarter of 2001,
skeptics immediately proclaimed the fall of the network business model that
Cisco exemplifies.
Ciscos vaunted supply chain systems were indeed meant to provide greater notice of impending demand slowdowns than they did in this case. But reports of the demise of the network modelin which companies go far beyond outsourcing and actually collaborate in the delivery of products and services to customersare much exaggerated. 'Network orchestrators' like Cisco might be experiencing their first real taste of adversity, but the network strategies they deploy look stronger than ever.
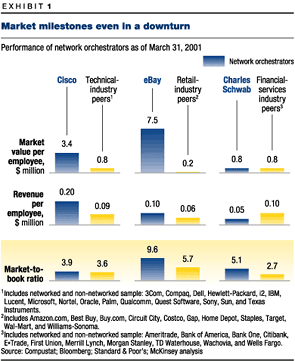
Indeed, Cisco outperformed its peers not only during the boom years of 1995 to 2000 but also during the first-quarter-2001 downturn (Exhibit 1). By most measures, its fellow network orchestratorssuch as Charles Schwab, CNET Networks, eBay, E*Trade, Palm, and Qualcommdid so as well. Our analysis shows that network orchestrators have reached their market milestones more quickly and earned greater value per employee than have their peers (see sidebar, 'Still looking good? '), and it suggests that they will continue to outperform other top companies inside and outside their industries. Because they own fewer assets and leverage the resources of partner companies, network orchestrators require less capital and return higher revenue per employee than do conventionally run companies, and they are better able to weather the damage usually inflicted by market volatility.
During the past decade, big corporations learned to dismantle, or 'unbundle,' themselves into their component parts, some of which they deemed to lie at the core of their business, while they sold off others. In so doing, however, they encountered a discomfiting question: if they were not exiting the business but would continue to deliver a complete product or service to customers, what would be their relationship with their former subsidiary or its marketplace counterparts?
As Cisco morphed into a virtual corporation during the 1990s, it answered that question by creating a 'gated network' of contract manufacturers and suppliers connected to one another and to itself by a powerful set of network applications running on its proprietary extranet. Cisco itself was disintegratingthat is, withdrawing from those parts of the industry value chain where it lacked preeminent advantagebut that didnt mean it was disengaging from the manufacturers, subcontractors, resource planners, and other companies on which the seamless delivery of its products to customers depended.
An information standard functions as a lingua franca, helping the partners to exchange information about customers and products
In fact, its network comprised a tightly disciplined group of businesses resembling a Japanese keiretsua bloc of interdependent companies operating within a given industry. Unlike keiretsu, however, a networks sinews are not cross-holdings of debt and equity but rather an information standard, which functions as a lingua franca, enabling network participants to exchange information about customers, products, schedules, inventories, costs, and almost any other data needed to serve those customers and create competitive advantage. (Networks differ from keiretsu in another respect as well: the customers themselves, being the generators of market information to which the businesses count on having instantaneous and broad access, are integral members of the network.) Whatever the information standard chosen, it facilitates interaction by specifying the ways in which information exchanged among the partners respective systems must be formatted.
Network orchestrators begin by undertaking a detached self-appraisal in which they identify those activities they do well enough to become the preeminent players in their marketseven though focusing on such activities might entail forgoing others that were already profitable or could become so.
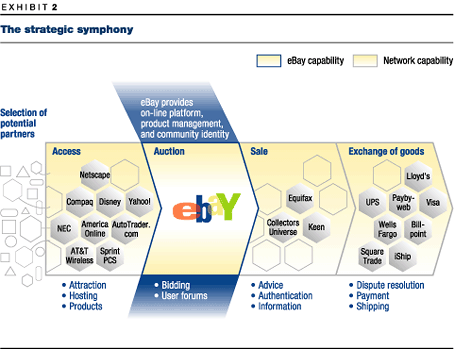
Orchestrators then set about establishing a platform across which the network participants will interact. For Cisco, this platform is the Cisco Connection Online, a World Wide Web-based channel for organizing and circulating information generated by the companys customers and partners. For eBay, the platform is the auction software that brings into being a community of sellers and buyers. In effect, eBay provides the product-management and distribution links of the value chain, while the companys specialist partners, such as Billpoint, iShip, Mail Boxes Etc., Tradenable, and UPS, handle direct payment, shipping, and other essential services (Exhibit 2).
For Charles Schwabs network, the platform is an
on-line system that refers customers to some 6,000 independent financial
advisers (handling a quarter of Schwabs assets under management) and provides
transaction services to those advisers. The platform has also made it possible
for Schwab to expand its range of products by distributing the mutual funds of
other institutions under its own banner and to engage E-Loan as a provider of
on-line lending services through the
Networks, of course, are not the only set of institutional relationships shaped by information technology. Microsofts Windows operating software places it at the center of an 'economic web' composed of companies that produce Windows-based software applications and related services for users of personal computers. The market position of a given company will determine which form suits it better. Companies more fitted to the role of network orchestrator do, however, enjoy certain advantages over those choosing to become shapers of economic webs.
Economic webs are the creatures of a Darwinian struggle in which several companies vie to establish a user base for their particular technologies. The technology that current users embrace becomes the 'standard' and thereby the choice of most new users. The sheer weight of the market preference for the platformrather than any alliance, agreement, or inducement offered by the platforms proprietoris the source of its influence over the economic webs existing members and of its ability to attract new ones.
Network orchestrators, by contrast, can control the circle of companies on which they depend even before, and indeed without, achieving overwhelming market acceptance. Demand for the manufacturers products and their number and complexity determine the proper sizethat is, the productive capacityof the network as well as its proper scope. Cisco, with a limited range of products and customers, maintains a well-defined network that mirrors a traditional manufacturing value chain; eBay, a service business with more diverse offerings and a larger number and assortment of customers, manages a more fluid, open-ended network.
Unlike economic webs, in which numbers equal power, networks are not open to all comers; the orchestrator invites companies in
Unlike economic webs, in which numbers equal power, networks are not open to all comers; rather, companies are invited into the network by the orchestrator. Whether these businesses then choose to join depends on their chances of doing three things: first, gaining access to the knowledge and expertise that the orchestrator derives from its unique perspective on the network members interactions; second, realizing efficiencies flowing from the network members sharing of assets; and, third, in the case of a service business like Schwab, obtaining privileged access to the orchestrators own customers.
While size is not an end in itself, as it is within economic webs, larger networks do have an easier time attracting additional partners, which bring new capabilities and customers and increase the odds that innovations will emerge. The presence of a greater number of participants in turn lowers transaction costs, amortizes risk, reduces the cost of tangible and intangible assets, and improves productivity.
The key tactical step for an economic-web shaper is to share the technology it wants to see become a standard with companies that, it hopes, will stimulate further demand for the technology by developing valuable applications. 'Sharing the standard' (usually by publishing the source code of the software involved) has become a revered new-economy precept: winning companies (such as Microsoft) do it; losing companies (Apple Computer) do not.
Orchestrators, however, do not share their core technologies. It is unnecessary for them to do so, since the viability of a network doesnt depend on its attracting a huge number of partners; moreover, the technology platforms of networks and economic webs dictate different relationships with their respective participants. One purpose of a network platform is to draw together participating companies by facilitating the exchange of information among them. The platform of an economic web, by contrast, being essentially a technical standard, merely makes it possible for companies to develop their complementary applications and has little effect on their organizational relationship with the shaper.
A network strategy thus enjoys important advantages over the economic-web strategies it superficially resembles. First, the orchestrator chooses both its partners and the standard, instead of depending on the market to embrace the standard it has chosen and then hoping that applications providers come around. Since market-based standards are harder to erect, broader in sweep, and thus fewer in number than proprietary networks, companies have a better chance of launching networks. Second, network orchestrators, being under no obligation to share their standard once it is established, are in a better position to manage and profit from their growth.
Before beginning to think about deploying a network strategy, managers must realize that not every company is cut out for the orchestrators role. Each company that has built a successful network began with a strong and close relationship with the ultimate consumer of the networks products. Unless a business has already created demand among end users and developed insight into their needs from having served them, it isnt likely to succeed in persuading other businesses to clamber onto its platform. A would-be network orchestrator will then of course have to promise them a continual flow of market intelligence and new strategic opportunitiesnot to mention lots of paying customers and a reasonable allocation of financial rewards.
Thus the strengths and limitations of some businesses might make them better suited to a specialists role within a network. In this role, too, companies can thrive. Companies that are equipped to serve as orchestrators will evaluate candidates for network membership on the basis of criteria such as size and maturity as well as their cultural and performance traits.
The following characteristics were present in every functioning network we studied:
It is also usually beneficial for members of manufacturing and distribution networks to devote most of their efforts and resources to the network.
The information exchange that standards facilitate most often concerns thorny, intercompany operational challenges. Let us say that a network orchestrator wants to give one of its business partners access to its customer accounts. The information that the partner seeks, such as orders, purchase histories, and demographics, probably resides in databases and directories on servers in the orchestrators IT systems. But these databases and directories will in many ways be different from the databases, directories, and servers in the partners call centers or shop floors needing such access.
Cisco, CNET, eBay, and other companies create standardized ways of presenting data so that computers communicate clearly
Cisco, CNET, eBay, and other companies create standardized ways of presenting this data so that computersand the people who use themcan communicate clearly. The orchestrator defines the schemas (common automated formats) that enable its business partners and customers to share information about themselves as well as purchase orders, shipping notices, invoices, forecasts, and credit authorizations. Much to the detriment of Covisint, the electronic marketplace for the auto industry, it neglected to establish standard ways of describing the thousands of types of parts found in the full range of automobile models that the marketplace serves.
Most companies that have made a go of building networks have been in the information technology business to begin with. Thus any company that aspires to be an orchestrator but lacks such a background would be well-advised to immerse itself in the underlying software that makes it possible to construct an information standard. The second step of such a company should be to evaluate what information is needed at each stage of the value chain and when. The third step would be to present that information in a clear and consistent way. Through trial and error, the standard and its requirements will be refined.
Either the customer or the orchestrator can enforce performance standards. In the case of eBay, both the sellers and the buyers rate each others conduct over the course of any given transaction by three criteria: disclosure, honesty, and fulfillment. The ratings themselves follow a rather simple three-point scale (+1, 0, -1). A cumulative score of -4 results in the suspension of the offenders eBay membership and exclusion from future transactions. In short, eBay does not set objective benchmarks for performance; rather, it lays out a system by which the participants subjectively rate one another. Like an auto parts marketplace that really works, it fashions words and numbers into an effective medium of communication.
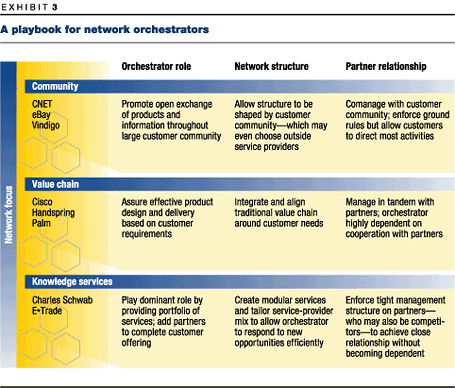
Charles Schwab, by contrast, monitors the performance of other network members (some of which are its competitors) and reserves the right to step in if a members performance or integrity falters and thus threatens Schwabs own brand. While Schwab benefits from the success of its partners, just as an economic-web shaper does, it may also try to learn how to do what they do so that, eventually, it can replace them. Other orchestrators define the relationship differently, usually according to where they fit within a rough typology (Exhibit 3).
Networks can flourish only if their orchestrators protect the welfare of all the companies on which they dependpartner or customer
A network thrives only if the orchestrator looks out for the welfare of all the companies on which it dependsbusiness partner or customer. Value-sharing mechanisms and incentives help ensure that kind of cooperation and build trust as well. Designed correctly, incentives can align the members behavior with the larger interests of the network, reducing the need for centralized control.
Cisco, for example, never splits revenue 50-50 with partners but instead divides it in their favor. By taking a smaller share, Cisco fosters the growth of the networks revenue and profits and ultimately enhances the value of its own stake. The company also provides nonfinancial incentives, such as free on-line training, marketing, and sales support, to those distributors that have generated high sales volumes or shown superior technical expertise. Billpoint and Tradenable, eBays direct-payment services, receive access not only to the auction companys community but also to customer feedback.
By drawing competitors into the network, Schwab also extends its own distribution channels and builds revenue. Its 6,000 independent investment advisers keep the fees they charge Schwab customers but pay an annual fee to be part of the network and, more important, generate more than $860 millionnearly 15 percent of Schwabs revenueby trading on the companys platform. Similar arrangements with E-Loan, Schwabs mortgage provider, and almost 150 outside mutual-fund companies (marketed under Schwabs OneSource brand) assure a full-service offering to customers and motivate the partners to increase the size and value of Schwabs network by bringing more assets under management. Thus Schwab wraps its name around the names of its competitors, which in return receive what is in effect the Schwab stamp of approval.
It is not enough for network orchestrators to create information standards. They must then use those standards to move their key business processesproject management, order entry, recruitment, human-resources administration, and budgetingon-line, where those processes can be made accessible to employees, partner companies, and customers. Cisco, for example, can give customers and suppliers real-time information on the status of an order (and can ensure, using a template, that orders are placed for technologically compatible equipment). By offering these benefits, as well as faster order fulfillment and lower prices, Cisco has been able to move 80 percent of its sales on-line. The number of its customers that cant find a suitable product has fallen, and its employees productivity has increased by 78 percent. Since 1998, Ciscos on-line order process has saved the company no less than $130 million a year.
Networks have the potential to move business ideas quickly across organizational boundaries
A network also has the potential to move business ideas quickly across organizational boundaries. Because product developers high up in the supply chain are suddenly in touch with the customer, they can carry out market tests and avoid straying far from their markets needs and tastes. And they hear the reactions of customers and business partners alike, allowing the networks members, as a group, to avoid the insularity and blindness that can afflict freestanding companies. The first customer service representatives of eBay, for example, were eBay customers whom the company invited to conferences and paid to support other customers. Today eBays Soapbox collects suggestions for enhancing network offerings, and trials are announced and discussed within the community.
Another example of collaboration is the
development, by the on-line brokerage E*Trade and the retailer Target, of
E*Trade Zones, which offer in-store customers access to trading and banking on
the World Wide Web. E*Trade Zones are now being launched in more than 200
Target stores in the
But to co-develop products and services effectively across a network, orchestrators must create cross-organizational teamssome ongoing, others dedicated to one-time projectswhich sometimes will be led by the orchestrators best-qualified partners, not by the orchestrator itself.
For 50 years or more, the scale and internal control of resources stood behind the prosperity of vertically integrated corporations. But recently, their very size and structure have slowed their responsiveness. Todays network leaders, by contrast, achieve remarkable success by leveraging the resources of their network partners. Unfortunately, such connectedness also makes the network leaders more vulnerable to their partners financial or logistical problems. Moreover, the transparency of networks can make participants in the supply chain overreact to what might be only temporary drops in customer demand. While the risk of inventory overhang is probably smaller among networked companies than their non-networked counterparts, the risk of ensuing shortages when demand revives may be greater. In the past, recoveries were often pretty far along by the time upstream players became aware that demand had earlier slackened.
Over the next few years, companies in many industries will form or join networks, which have not only the levels of integration and internal transparency of very large companies but also the openness to market information and the flexibility in responding to it that are the strong suit of small, young ones. In addition, networks give their organizers competitive scale, which they achieve not by taking the expensive route of mergers and acquisitions but by turning their suppliers, subcontractors, and, sometimes, their competitors into close collaborators.
Building a platform and then using it to govern a network might sound good in theory, but how strong are the financial results this approach delivers? Charles Schwab, Cisco Systems, CNET Networks, eBay, E*Trade, Palm, and other members of the first generation of network orchestrators have outperformed their peersleaders in their industriesin most key measures of revenue growth and the creation of shareholder value. More impressive, they achieved such growth and value creation with smaller asset bases and higher employee productivity (exhibit, part 1).
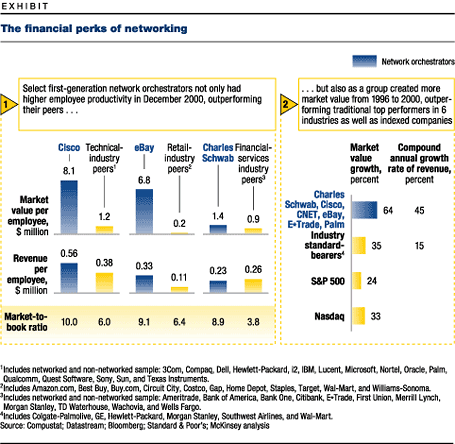
In our analysis, we also compared the network orchestrators performance with that of market leaders in six industry segments (commercial airlines, consumer products, financial services, high technology, industrial products, and retailing). This group, identified by previous McKinsey research as top performers in their industries over 30 years, was then culled for sector leaders in the period from 1996 to 2000, when networked companies took root. Network orchestrators far outperformed these industry standard-bearers, as well as the NASDAQ and S&P 500 listed companies, in both shareholder value creation and revenue per employee (exhibit, part 2). And as we have already mentioned, almost every measure of performance suggests that the leading network orchestrators, including Cisco, maintained their advantage even in a broad market decline.
This is how particular companies fared:
From 1995 to 2000, Schwabs net income grew by 27 percent a year, though the firm made no large acquisitions. At the end of the year 2000, Schwabs market-to-book ratio was 8.9more than double the ratio of almost all of its closest competitors. As of March 2001, this ratio was still almost twice that of the rest of the industry (although Schwabs revenue per employee lagged slightly behind the industry norm).
During the same period, Ciscos revenue grew by an average annual rate of 57 percent, and its market value per employee more than tripledto $8.1 million, from $2.3 million. (Networks and their beneficial effects are doubtless responsible for the performance of technology companies boasting even higher numbers: Palm, with $11.5 million in market value per employee, and Qualcomm, with $9.5 million.) As of March 2001, Ciscos revenue per employee was still more than twice that of other industry leaders.
The revenue of eBay grew by an annual average of 92 percent from 1996, its founding year, when its revenue stood at $32 million, to 2000, when its revenue had risen to $431 million. At the end of 2000, eBays market-to-book ratio of 9.1 was by far the highest in the retail industry. Indeed, eBay had created $6.8 million of market value per employee30 times the industry average and about 10 times that of Amazon.com, which is not a network orchestrator. As of March 2001, eBays market-to-book ratio had grown to 9.6, almost twice the industry norm, and its market value per employee, at $7.5 million, dwarfed that of competitors.
Remo Hcki is a consultant in
McKinseys
The authors would like to thank Parke Boneysteele, Elin Eifler, John Hagel III, J. V. Ramakant, Marc Singer, Robert Ward, and Mark Watson for their invaluable contributions to this article.
Paul Krugman, 'Chip of fools,' New
York Times,
See John Hagel III and Marc Singer, 'Unbundling the corporation,' The McKinsey Quarterly, 2000 Number 3, pp. 14861.
See John Hagel III, 'Spider versus spider,' The McKinsey Quarterly, 1996 Number 1, pp. 418, and On Strategy, a McKinsey Quarterly anthology, 2000, pp. 7180.
For instance, DXML (Dynamic Extensible Markup Language), LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol), SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol), UDDI (Universal Description Discovery and Integration), WSDL (Web Services Description Language), and XML (Extensible Markup Language).
|
Politica de confidentialitate | Termeni si conditii de utilizare |

Vizualizari: 1180
Importanta: ![]()
Termeni si conditii de utilizare | Contact
© SCRIGROUP 2024 . All rights reserved