| CATEGORII DOCUMENTE |
| Bulgara | Ceha slovaca | Croata | Engleza | Estona | Finlandeza | Franceza |
| Germana | Italiana | Letona | Lituaniana | Maghiara | Olandeza | Poloneza |
| Sarba | Slovena | Spaniola | Suedeza | Turca | Ucraineana |
DATA COMMUNICATIONS
The purpose of this Lesson is to discuss Data Communications.
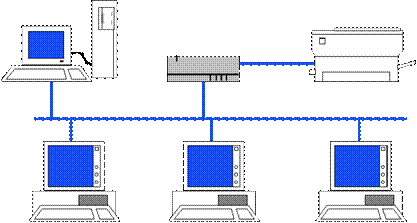
Data Communications is the exchange of information between computers and other devices, including,
Integrated Circuits,
Sub-sections,
PC Boards,
other computers,
peripherals
circuits &
controllers
2 Categories of
Data Communications
1. Local
The computer & devices are directly connected.
(hardwired or internal)
2. Remote
The computer & devices are indirectly connected.
(thru telephone or satellite etc.)
__________ ______ ____ _____ _______ ______ ______
These Categories of Data Communications include:
Parallel Interconnection Standards
& Serial Interconnection Standards
Parallel Standards are used for local communication.
Serial Standards are used for remote communication.
__________ ______ ____ _____ _______ ______ ______
Parallel Interconnection Standards include,
IEEE-488 Instrumentation Bus Standard,
S-100 Hobbyist Bus Standard
IBM-PC Bus Standard
Centronics Printer Connection Standard
And many others
__________ ______ ____ _____ _______ ______ ______
Serial Interconnection Standards include,
Current
RS-232C,
RS-241,
XMODEM,
YMODEM, &
ZMODEM
__________ ______ ____ _____ _______ ______ ______
There are 3 Terms describing
Data Communications Capabilities
1. Simplex
2. Half-Duplex One Way at a Time (Police Radio)
3. Full-Duplex Both Ways Simultaneously (telephone)
__________ ______ ____ _____ _______ ______ ______
The rates of data transmission
are described in terms of;
BPS Bits Per Second (Data Bits only)
&/or Baud Rate Data & Sync. bits per sec
Pieces of information per sec
There are
2 major types of
information modulation
commonly used
AM Amplitude Modulation.
& 2. FM Frequency Modulation.
__________ ______ ____ _____ _______ ______ ______
For,
Amplitude Modulation AM
A single frequency is;
turned-on to indicate a '1',
turned-off to indicate a '0'
This Method resembles Telegraph Code
__________ ______ ____ _____ _______ ______ ______
And for,
Frequency Modulation FM
2 specific types of FM
FSK - Frequency Shift Keying, which uses,
1 tone for '1'
another for '0'
PSK - Phase Shift Keying, which uses,
1 phase-shift for '1'
another for '0'
__________ ______ ____ _____ _______ ______ ______
There are
2 Categories of
Serial Data Communication
1. Asynchronous
& 2. Sychronous
__________ ______ ____ _____ _______ ______ ______
Asynchronous (Below 10,000 bps)
In this category, one character is transmitted at a time, with synchronization included. (LSB 1st)
Each character is FRAMED by adding START & STOP bits, adding another 20% to the total time. (They're also called mark & space bits )
__________ ______ ____ _____ _______ ______ ______
The START bit is the1st negative edge of the frame.
A STOP bit is represented by a HI for 2 time periods at the end of each character.
__________ ______ ____ _____ _______ ______ ______
Synchronous (Up to 20,000 bps)
Each user synchronizes tranmission with the other.
In this category, many characters are sent at a time in block form.
Each block is identified by start & end characters.
IC'S commonly used in these circuits include;
a. MC6830 ACIA
b. 8250 UART
c. 8251 USART
. ..d. 8291.. IEEE-488
__________ ______ ____ _____ _______ ______ ______
Error Detection & Correction Methods
Retransmission
Just retransmit the data
& Parity Checking Methods
Bit-counting Techniques
__________ ______ ____ _____ _______ ______ ______
Parity Checking Methods include,
a. Check Sum
Parity sum sent with data
b. Cyclic Redundancy Checking
A Parity Sum quotient fraction is sent with data.
c. Hamming Code
Similar to Check Sum with added bits.
d. Matrix Sum
Parity Sum set into a matrix. (LRC/VRC)
NETWORKS.
The purpose of this Lesson is to discuss Networks.

A Computer NETWORK is the interconnection of several Computers for the purpose of sharing information &/or resources.
__________ ______ ____ _____ _______ ______ ______
4 Basic Network Types,
which link many microcomputers together:
1. LANs Local Area Networks;
2. MANs Metropolitan Area Networks
3. WANs Wide Area Networks
4. SNAs System Network Architectures;
Let's discuss each of these one at a time
__________ ______ ____ _____ _______ ______ ______

LANs.
Local Area Networks usually connect computers together by Common Data Transmission Medium, that are in a single building or on a single campus. (Less than 10 Kilometers.)
In NETWORK discussions, the term FILE-SERVER often arises.
A FILE-SERVER is, simply, a dedicated Microcomputer, whose function is to SERVE the members of a Network.
MANs.
Metropolitan Area Networks are capable of Hi-Speed Data Communications and connect computers together, that are within the same Metropolitan Area (10 to 80 Kilometers.)
WANs.
Wide Area
Networks connect computers together by common carrier, that
may be very far apart in
SNAs.
System Network Architectures links PC's to mainframe computers. (IBMs mainframe standard)
There are several of these business-dedicated Networks in use in the world, but, needless to say, they are not in the public domain.
__________ ______ ____ _____ _______ ______ ______
The Network Topology
describes HOW Computers are connected together to exchange information.
__________ ______ ____ _____ _______ ______ ______
The 3 connection-types are called TOPOLOGYs
The 3 most common means of network inter-connection are,
a. BUS Topology
Computers share a bus, where each may drop-off or pick-up information.
b. STAR Topology
(Parallel) (Token Ring)
All computers are connected to a central brain or coordinator.
c. RING Topology
(Series) (Cascaded Star)
Computers are daisy-chained together.
__________ ______ ____ ________________
A Network, besides the Connections and users themselves, consists of,
HARDWARE including
Network Interface Cards,
& Network Connecting Cables
SOFTWARE including
Protocol Software
Network Operating System Software,
& Network Software
to run end-user programs
__________ ______ ____ _____ _______ ______ ______
Let's discuss them, one at a time
NETWORK HARDWARE
Network Interface Cards
The purpose of Network Interface Cards is to provide the physical connection for the computer to the Network.
The Network Interface Card must,
1. Get Computer Data
2. Format Computer Data
3. Encode Computer Data
4. Get access to the Network Cable
5. Establish the lines of communications by providing the HANDSHAKING.
__________ ______ ____ _____ _______ ______ ______

The 3 ways to move Data between the Computer & the Network Interface Card are,
DMA
I/O
& Shared Memory
__________ ______ ____ _____ _______ ______ ______
The Network Interface Card & its Software determine Network SPEED.
At the other end, the transceiver waits for the Data & the whole process happens in reverse. The Data is
1. Demodulated
2. Decoded
3.Converted (from Serial, back to Parallel)
4. Depacketized &
5. Made READABLE
__________ ______ ____ _____ _______ ______ ______
Connecting Cables
Network InterConnection is often done by Cable, although Microwave Transmission IS used.
These connections are accomplished by,
Coaxial Cable,
Twisted Pair,
Fiber Optics
Each one has its advantages & disadvantages
__________ ______ ____ _____ _______ ______ ______
NETWORK SOFTWARE.
Protocol Software,
Protocol is the set of rules, provided by Software, that governs communication between computers.
Protocols govern, Data & Handshaking,
1. Format
2. Timing
3. Sequence
4. Error Control
__________ ______ ____ _____ _______ ______ ______
Protocols are divided into 7 layers
by the Open System Interconnection (OSI) Model to allow different Protocol Standards to work together. These are,
LAYER PURPOSE
1. Physical .Defines Cable Characteristics
2. Data-Link .Data Blocks,Sync,Error & Flow Control
3. Network .Establishes,Maintains,Terminates Connection
4. Transport .Checks for Data OK
5. Session .Establishes Conversations
6. Presentation ..Code Conversion,Data Reformat
7. Application .Supplies Functions to Computer
__________ ______ ____ _____ _______ ______ ______
Network Operating System Software,
A Network Operating System makes a collection of independent Computers act as ONE System.
Network Operating Systems provide,
1. Resource Sharing Capabilities
2. Data Integrity
3. Security
4. Administrative Tools
5. Troubleshooting Tools
6. Multi-Network Support
__________ ______ ____ _____ _______ ______ ______
Network Operating Systems
being used include,
Novell NetWare
Banyan VINES
DCA
ArcNet
EtherNet
__________ ______ ____ _____ _______ ______ ______
Of course, any of the dedicated Application Program software, that were discussed in earlier Lessons, can be used to process information, after it has been recovered by the System.
__________ ______ ____ _________
MODEMs
The purpose of this Lesson is to discuss MODEMs
MODEM stands for
MODulator/DEModulator.
A modem is a device used by computers to communicate with each other over standard telephone lines.
Modems convert digital signals from the computer into audio frequencies within the bandwidth of a telephone.
__________ ______ ____ _____ _______ ______ ______

MODEM TYPES.
MODEMs are available as either,
1. INTERNAL
A PC Board that plugs into an Expansion Slot
or 2. EXTERNAL
A separate Unit, that can be switched or moved as needed.
__________ ______ ____ _____ _______ ______ ______
Modems are also classified by speed
The speed of a MODEM can be given as Bits Per Second (bps) or as its Baud Rate.
Bits Per Second refers to Data Bits only
Baud rate is bps including start & stop bits
It is also defined as the total number of Flux Changes Per Second.
__________ ______ ____ _____ _______ ______ ______
Let's see the SPEED Classifications.
MODEM SPEED CLASSIFICATIONS
Lo spd = 1 - 600 bps (No Longer Used)
Med spd 600 - 2400 bps .. (Common
Hi spd = 24K-30,000 bps (Most Common)
Above 19,000 bps a wide-band Modem & channel is required.
Using special data packaging techniques, the BPS actually realized may be much higher.
We'll see HOW that can be, but first,
There are other considerations involved with MODEM information exchange. They are
1. Protocols
2. Handshaking &
3. Type of Communication
__________ ______ ____ _____ _______ ______ ______
Terms
Synchronous or Asynchronous
Half or Full Duplex, etc
FM, QAM, Bits, Dibits, or Tribits
__________ ______ ____ _____ _______ ______ ______
PROTOCOLS.
A Protocol is the established procedure for exchanging Data along with instructions that coordinate the process.
Most Protocols are error-correcting and use one or more of the error-correcting techniques already discussed.
The most-used of these include,
PROTOCOL - TRANSMISSION TECHNIQUE
XMODEM..1/2 Duplex PSK.
YMODEM 1/2 Duplex PSK
MODEM Full Duplex QAM
KERMIT Full Duplex QAM
BLAST Full Duplex QAM
JMODEM Full Duplex QAM
BiMODEM Full Duplex QAM
Sealink Full Duplex QAM
Telink 1/2 Duplex PSK
Almost all of these use CRC & Checksum Error Detection and will automatically request retransmission upon Error Detection.
__________ ______ ____ _____ _______ ______ ______

MODEMs
TECHNIQUE OF TRANSMISSION.
For MODEMs, AM was never used. FM Techniques like FSK & PSK were initially used often.
The original FSK
standard was the
Half-Duplex MODEMs use PSK Techniques
1 Phase Shift is a , Another is a
__________ ______ ____ _____ _______ ______ ______
QAM, Dibits & Tribits
Nowadays, Full Duplex MODEMs use QAM.
QAM stands for Quadrature Amplitude Modulation.
It is a type of Phase Modulated FM, in which a Dibit, (2 Bits), are encoded together.
Quadrature means 90 degrees out of phase
Binary 00,01,10,& 11 or Decimal 0,1,2,& 3 are encoded by 1 of 4 Phase Shifts.
Tribits are encoded, similarly. Remember,
There are 2 Categories of Serial Data Communication Which MODEMs use,
1. Asynchronous
& 2. Sychronous
__________ ______ ____ _____ _______ ______ ______
Asynchronous (Below 10,000 bps)
In this category, one character is transmitted at a time, with synchronization included (LSB 1st).
____________________
Each character is FRAMED by adding START & STOP bits, adding another 20% to the total time. (They're also called mark & space bits.)
____________________
The START bit is the 1st negative edge of the frame.
A STOP bit is represented by a HI for 2 time periods at the end of each character.
__________ ______ ____ _____________
Synchronous (Up to 20,000 bps)
a. Each data handler person synchronizes with the other
b. In this category, many characters are sent at a time in block form.
Each block is identified by start & end characters
__________ ______ ____ ______________
STEPS IN MAKING CONTACT
In order for a Computer to exchange information with another computer, CONTACT must be established between them.
To establish contact,
1. Initialize the MODEM
2. Dial the telephone number
3. Wait for answer carrier
4. Send originate carrier
5. Report MODEMs locked-on
& TO ANSWER AN INCOMING CALL
1. Initialize the MODEM
2. Answer on specified ring
3. Provide the answer carrier
4. Listen for an Originate carrier
5. Report MODEMs locked-on
In order to establish the lines of communication between one computer & another, an orderly process must be used to ensure that data is transmitted only when the other party is READY for it.
This process is known better as,
HANDSHAKING
__________ ______ ____ _____ _______ ______ ______
MODEM CONTROL SIGNALS
MODEM Control Signals include,
Abbrev Name Meaning
DTR Data Terminal Ready Computer Ready
DSR Data Set Ready MODEM Ready
DCD Data Carrier Detect Remote MODEM on-line & ready
RI Ring Indicator Modem senses ringing
RTS Request To Send Computer to MODEM,OK/Send?
CTS Clear To Send MODEM to Computer,Go Ahead
TD Transmit Data Actual Outbound Data
RD Receive Data Incoming Data
The MODEM may need DTR from the Computer before permitting Data Exchange.
The Communications Program may need DSR from the MODEM before permitting Data Exchange.
The computer sends RTS and only after the MODEM responds with CTS can a computer transmit data.
Even though that's what's supposed to happen, in reality, many office computer systems connect to MODEMs that only have 3 wires. For,
Transmit Data
Receive Data &
Ground
__________ ______ ____ _____ _______ ______ ______
MODEM CIRCUITRY.
A MODEM has several sections, some optional
The vital circuits are,
Section Ckt Purpose
I/O INTERFACE ..,,For V & I level adjustment
OUT MODULATOR D-A Conversion & VCO output
IN DEMODULATOR A-D Conversion & VCO Phase Reference
I/O .FILTERS To remove unwanted noise
I/O AMPLIFIERS To ensure adequate Gain
I/O TRANSFORMER Telephone Line Isolation, Z-Matching
__________ ______ ____ _____ _______ ______ ______
SENDING DATA
Information to be sent comes from the Computer, and is Level-adjusted by the INTERFACE Circuit.
It is then passed to the MODULATOR Circuit.
The Modulator converts the DIGITAL Data into an Analog Voltage which is used to vary the Frequency of the Voltage Controlled Oscillator (VCO).
The VCO Output is, then, FILTERED, AMPLIFIED & applied to the Telephone Line Isolation TRANSFORMER, where it travels to its destination.
__________ ______ ____ _____ _______ ______ ______

RECEIVING DATA
Received information comes through the Telephone Line Isolation Transformer, is FILTERED & AMPLIFIED before being applied to the DEMODULATOR.
The job of the DEMODULATOR is to convert the Analog Signal back into Usable Digital Data.
This is performed by comparing the phase & frequency of the incoming signal to the phase & frequency of the local VCO.
This Phase Comparator Output is then applied to the INTERFACE circuit, which Holds it for Computer Processing.
IC'S commonly used in Telecommunication circuits include;
IC # .. TYPE USED for,
a. MC6830 ACIA PORTs
b. UART PORTs
c. NS16450 UART MODEMs
d. NS16550 UART MODEMs
c. USART PORTs
d. IEEE-488 Parallel Instrumentation
|
Politica de confidentialitate | Termeni si conditii de utilizare |

Vizualizari: 1642
Importanta: ![]()
Termeni si conditii de utilizare | Contact
© SCRIGROUP 2025 . All rights reserved