| CATEGORII DOCUMENTE |
| Bulgara | Ceha slovaca | Croata | Engleza | Estona | Finlandeza | Franceza |
| Germana | Italiana | Letona | Lituaniana | Maghiara | Olandeza | Poloneza |
| Sarba | Slovena | Spaniola | Suedeza | Turca | Ucraineana |
Islamic Architecture
Plan of Mosque:
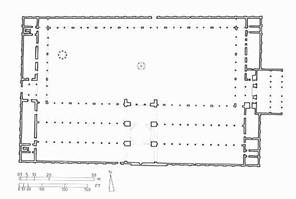 Great
Mosque at
Great
Mosque at
Exterior of Mosque- primary place of worship
Box shaped or basilican shaped (Byzantine influence, Early Christian influence)
Square, tall towers- call to prayer from minarets
Courtyards
Long east-west axis
-relatively
plain on exterior (Kufa), but moved to
-exterior is not monumental yet
v Mosques different in various parts of Muslim world shape wise.
Arab vs. Muslim
Arabs:
624 AD direction of prayer changes
from
Nationalizes religion for Arabs
Islam = submission to will of God
Five Pillars of Islam:
Shahada or profession of faith
Simple statement of faith
There is no god but Allah and Mohammed is his prophet.
Daily Prayer
5 times a day from early morning to evening
Facing
Principal prayers Friday noon
Provision for prayer fundamental in mosque design
Almsgiving
More important than in Christianity
Led to large number of architectural dedications
Fasting during month of Ramadan
Necessary to abstain from food, drink, sex
Difficult during daylight hours
Follows lunar calendar so varies during solar years
Pilgrimage
to
Trip to
Haj (pilgrimage) noted in house decoration of those who make journey
Umayyad vs. Abbassid periods:
Umayyad= Caliphate of
Abassid= Caliphate of
Qibla:
-the prayer wall
-the direction that should be faced when a Muslim prays
-most mosques have a niche in the wall that indicates the qibla
-once was
in
Madrasa:
-an Islamic religious school
-did not exist in early times, school held in mosques
-courts located parallel to the qibla, thus continuing an established tradition of incorporating education with worship (law and religion = higher education)
Important Buildings:
House of Mohammad, House of the Prophet in
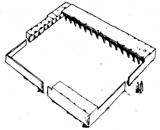
Basic elements:
-Sahn or courtyard
-source of water for cleansing
-call to prayer from minaret
-Mimbar or speakers platform
-prayer hall and quibla wall
-Quibla aisle and transverse aisle
-prayer hall facade
Mosque of Kufa
640 AD
Basic elements:
-reversal of position of prayer hall from one side of court to other
-increased numbers of living units
Great Mosque of
 706-14 AD
706-14 AD
Basic elements:
-plan follows basilican shape of Syrian Christian church
-long east-west axis used for rank and file organization of congregations
-reuse of church, door opened in north wall
-representative of mosques in Christian west
-minaret
developed form corner
-mihrab in qibla wall from apse of Christian church
Dome of Rock
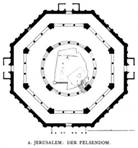

Basic Elements:
-source of building type in Byzantine arch
-centralized plan popular for tomb, baptistery, martyrium
-rubber walls with interior columnar supports carrying wooden roof
-double octagon of inner and outer series of piers
-focus of center of rock beneath dome
-interpretation of mosaics and inscriptions
-inscriptions from Koran emphasize victory of Islam over Children of the Book
-decorative elements and symbols of royal houses of defeated peoples
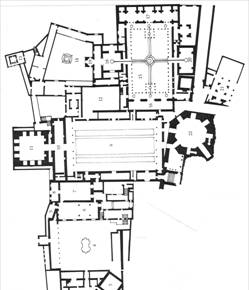
Principles:
-built over long period of time but many different kings (300yrs)
-irregular terrain and change of grade levels
-sequence and ceremony
-no faade
-no destination
-materials included strong fortified walls of stone, timber and plaster
-Parallel and perpendicular axes- no system of organization
-water systems
-gardens
-Ornament- wood, marble, plaster, metal, arches, screens, channels
-bright light, layers of space with varying light
-
-private v. public space
|
Politica de confidentialitate | Termeni si conditii de utilizare |

Vizualizari: 1889
Importanta: ![]()
Termeni si conditii de utilizare | Contact
© SCRIGROUP 2025 . All rights reserved