| CATEGORII DOCUMENTE |
| Bulgara | Ceha slovaca | Croata | Engleza | Estona | Finlandeza | Franceza |
| Germana | Italiana | Letona | Lituaniana | Maghiara | Olandeza | Poloneza |
| Sarba | Slovena | Spaniola | Suedeza | Turca | Ucraineana |
Motors are used to drive loads. The purpose of a motor control system is to control the speed or position of the load. A control system does this by changing the voltage or current which supplies the motor in response to an input signal. Input signals can be manual, such as an operator pressing a button, or from another controller, such as a signal from a PLC.
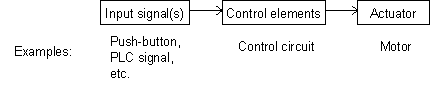
Fig. 30 Generic control scheme
Control systems may be open loop or closed loop.
In an open loop motor control system, the electrical and mechanical characteristics of the motor being controlled are well known. For example: a certain voltage applied to the motor will produce a certain rotor speed. The open loop controller is designed to apply a certain voltage or current to the motor in response to a certain input.
Should the characteristic of the motor change then the controller needs to be changed, otherwise there may be errors in controlling the load.
Example
A motor has the following characteristic: an input of 50 volts produces an output of 1000 rpm. A controller designed to run the motor at 1000 rpm supplies 50 volts to the motor. If the weight of motor load doubles, then the same voltage from the controller might only produce 850 rpm. The change in the mechanical characteristics of the load causes an error between the desired speed and the actual speed.
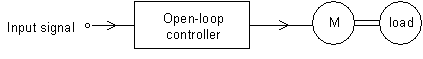
Fig. 31 An open loop controller uses an input signal to drive a motor
The advantage of an open loop system is its simplicity. The disadvantage is that the controller does not adapt to changes in the motor characteristics, and any errors must be manually corrected.
Controllers can be made more sophisticated if information about the load being controlled is known. Useful information is the speed of the load and its position. Sensors used for measuring these quantities include tachometers, potentiometers and encoders.
Tachometers - the tachometer is used for measuring speed of rotation. It produces a voltage which is proportional to the speed of rotation of its shaft. If the speed of rotation doubles, the voltage output of the tachometer doubles. Tachometers are also known as tacho-generators.
Potentiometers - the potentiometer is used for measuring angular or linear position. It produces a voltage proportional to its absolute position.
Absolute Encoders - the absolute encoder is used for measuring angular position. Depending on its resolution or accuracy, each angular position of the motor shaft will produce a specific output signal.
Incremental Encoders - the incremental encoder is used for measuring speed or relative position. The incremental encoder outputs pulses at regular angular intervals of the motor shaft position. When the motor speeds up, the incremental encoder outputs pulses more often. Measuring the frequency at which pulses are produced indicates the speed of the motor. Counting the number of pulses sent by the encoder indicates the distance through which the motor shaft has moved.
In a closed loop system, sensors measure outputs such as load speed and position. The sensed output signals are compared with the desired output, and the controller supplies a correcting signal.
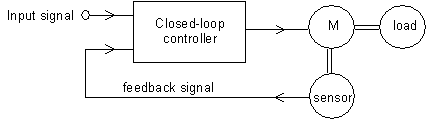
Fig. 32 A closed loop controller uses an input signal and feedback from sensors to drive a motor.
The controller uses the feedback signals to supply a new signal to the motor. This new signal drives the motor towards the desired output.
The advantage of a closed loop system is the high accuracy which is achievable. The output is continually monitored and controlled. The disadvantage is the complexity of the system, as more components and wiring are needed.
A servo system is a closed loop control system.
Servo systems consist of a number of components:
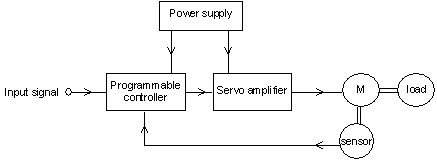
Fig. 33 A servo system
Servo systems can be adapted to suit the load being controlled. For example: a motor may have to be controlled very quickly or very accurately. Depending on its complexity, the servo system is tuned or compensated to achieve these results.
A servo system can be constructed by choosing suitable sensors to match the motors in the system. A better method is to use a servo motor. A servo motor is a motor with a feedback sensor already attached. The advantage of using purpose-made servo motors over individual components is that the sensors are guaranteed to be matched to the motor being used, and each sensor is properly coupled to each motor.
Both AC and DC motors are used in servo systems.
The advantages of servo motors are high performance, small sizes and the wide variety of components available. The disadvantages are the higher cost of servo systems, and limitations on performance imposed by controller technology.
|
Politica de confidentialitate | Termeni si conditii de utilizare |

Vizualizari: 1349
Importanta: ![]()
Termeni si conditii de utilizare | Contact
© SCRIGROUP 2025 . All rights reserved